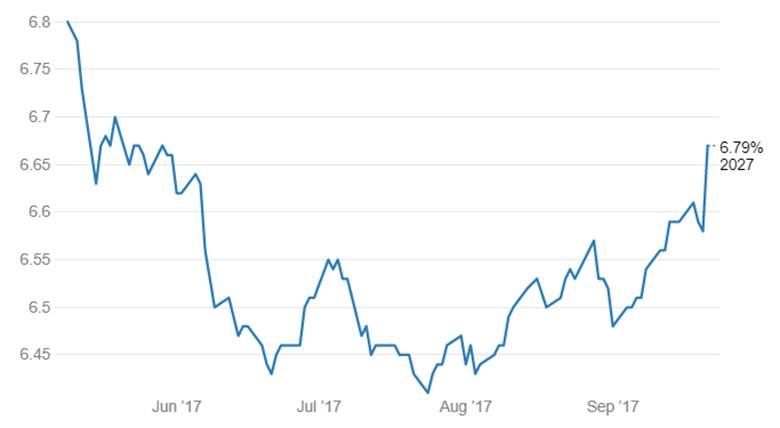
India’s benchmark 10-year G-sec, the 6.79% 2027 G-sec, rose to 4 months highs of 6.67% (Chart 1) as the market is concerned about Government fiscal stimulus plan, Fed rate hikes and balance sheet unwinding and CPI Inflation that could derail rate cuts in RBI October 2017 policy review.
The bond market will be nervous going into RBI October policy review but a sustained spike in G-sec yields is not on the cards given that there is high liquidity in the system that can absorb government borrowing if the government resorts to market borrowings to fund its fiscal stimulus plan, Fed has guided for a slow and gradual pace of rate hikes and balance sheet unwinding and inflation expectations are muted and RBI will keep rates low given high real interest rates in the economy.
G-sec yields are likely to trade nervously until the dust settles on the three factors and would then move down on buying at higher levels.
10-year G-sec Movement
Three Factors which are Hammering 10-Year G-sec Prices
1 Inflation
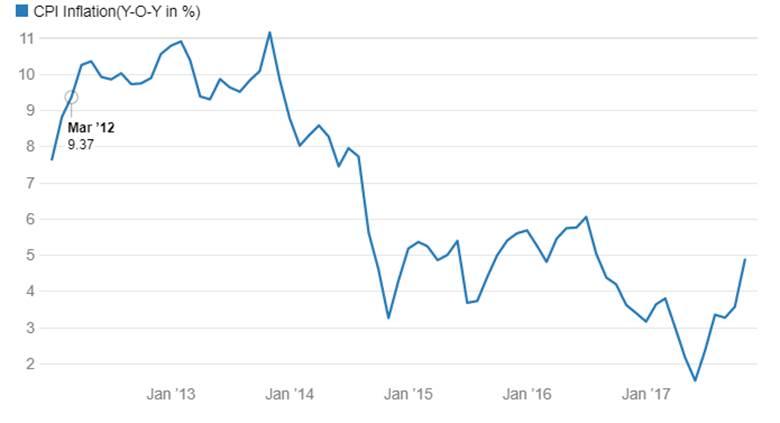
After the implementation of Demonetization and GST, inflation fell to record low of 1.54% in June 2017 (mainly due to destocking of goods), July & August inflation data suggest an uptick in inflation mainly due to monsoon disruptions and increase in retail fuel prices. CPI in August 2017 rose to 3.36% from 2.36% in July 2017 (Chart 2)
CPI Inflation(Y-O-Y in %)
2 Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit for July 2017 came in at 92.4% of Budget Estimates for 2017-18, For this fiscal year Government has set a target of 3.2% of GDP.
Due to Demonetisation and GST implementation, economic growth has fallen, recent GDP data showed that India’s GDP grew by 5.7% in Q1 2017-18, GDP growth fell to 3 year low s(Chart 3). In order to boost economic growth, the Government is planning a fiscal stimulus and the market is concerned that India’s fiscal deficit could widen if Government opted for a fiscal push. Media reports suggest that the Government is planning for Rs. 650 billion stimulus to the economy and one of the options to fund the stimulus is through market borrowings.
3 US Federal Reserve Rate Hike and Balance Sheet Unwinding
Federal Reserve in its September policy meets kept interest rates unchanged but guided for 1 more rate hike in 2017 if inflation picks up. Fed also suggested that it will raise rates by two to three times in 2018 and 2019 if inflation holds to its own forecasts.
Federal Reserve will also start unwinding its $4.5 trillion balance sheet in October 2017, initially by $10 billion per month, unwinding of the balance sheet could decrease the liquidity gradually.