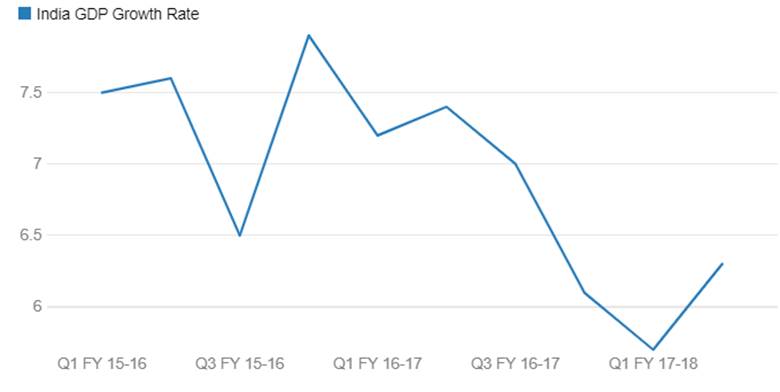
India’s GDP growth for the 1st quarter of fiscal 2017-18 came in weak with a growth of 5.7% against 6.1% seen in the 4th quarter of fiscal 2016-17. The first quarter growth was the weakest quarterly growth seen since the base year was changed from 2004-05 to 2011-12. Growth would have been weaker if not for government front loading its spending. The government has touched 92.4% of its fiscal deficit target as of July 2017. GST, which was introduction in July 2017 ,led to manufacturing activity slowdown as producers destocked inventories in the first quarter of fiscal 2017-18. Nominal GDP grew by 9.3% against targeted levels of 11.5%.
In order to boost economic growth, the Government is planning a fiscal stimulus and the market is concerned that India’s fiscal deficit could widen if Government opted for a fiscal push. The Government announced a Power Sector push to supply electricity for all households, costing Rs 160 billion. The government is to take a decision on a Rs. 650 billion stimulus to the economy. One of the options to fund the stimulus is through market borrowings which can disturb the fiscal consolidation path.
Fiscal stimulus is not necessary as Indian economy is into transitory phase. The government should continue to carry out reforms as the macroeconomic parameters are extremely comfortable with current account deficit (CAD) at 2.4% of GDP as of 1st quarter of fiscal 2017-18 followed by fiscal deficit targeted at 3.2% of GDP for 2017-18, CPI inflation at below 4% levels and forex reserves at all-time highs of USD 402 billion.
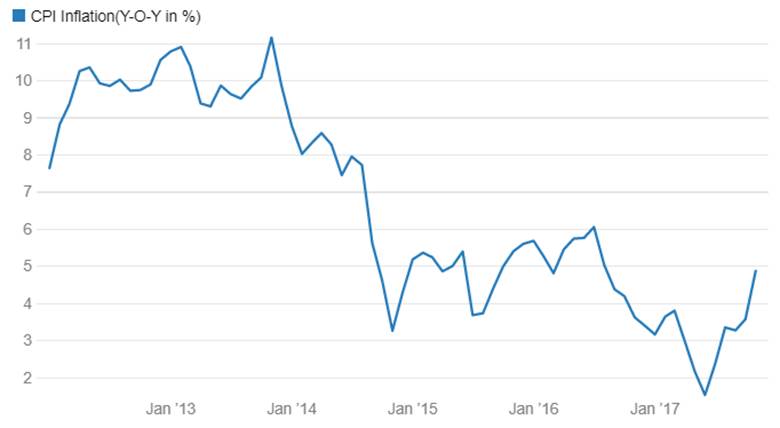
CPI inflation is on a downward path from year 2014-15. Inflation has come down to 3.36% in August 2017 from levels of 9.5% seen in year 2013-14. In June 2017 policy , RBI maintained its neutral stance and its 4% CPI inflation target though it stated that CPI inflation could fall well below its forecast of 4.5% to 5% for this fiscal year. RBI has forecast inflation at 2% to 3.5% for the 1st half and 3.5% to 4.5% for the second half of the year.
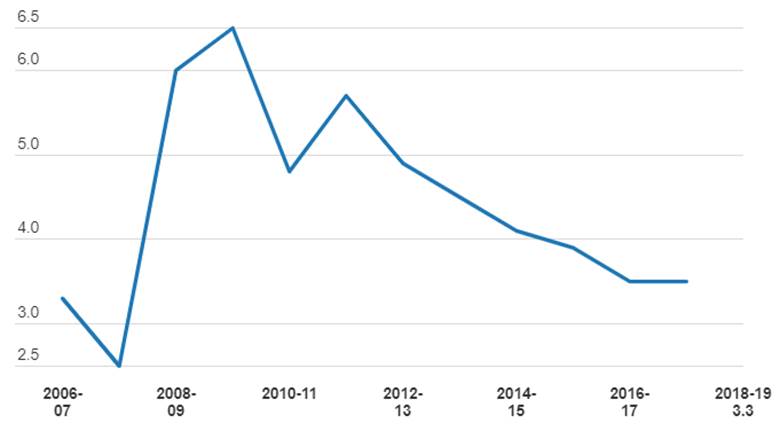
Fiscal deficit as percentage of GDP has come off from 4.5% levels seen in year 2013-14 to 3.2% levels as of fiscal 2016-17 helped by government policies to control the deficit. The government is targeting a fiscal deficit of 3.2% of GDP for the fiscal years 2017-18 and 3% in 2018-19.
CAD was at USD 14.3 billion in the 1st qtr of this fiscal year against USD 0.4 billion in 1st qtr of fiscal 2016-17 and USD 3.4 billion 4th quarter of last fiscal, Sharp rise in FDI and FII inflows at USD 7.2 billion (USD 3.9 billion in 1st qtr of fiscal 2016-17) and USD 12.5 billion (USD 2.1 billion in 1st qtr of fiscal 2016-17) more than made up for the rise in CAD. India’s current account deficit (CAD) at 2.4% of GDP as of 1st quarter of fiscal 2017-18 is sustainable compared to CAD of 4.8% of GDP in 2013-14.
India GDP Growth
CPI Inflation(Y-O-Y in %)
India Fiscal deficit (% of GDP)
In the last 4 years since September 2013, Sensex has risen 58% to record high levels. Reasons for driving flows into equities are
· Low global and domestic interest rates
· High global and domestic liquidity
· Stable macroeconomic data
· Strong earnings growth in auto,transportation, retail, agri products, downstream oil & gas
· Strong FII flows into equities (USD 37 billion)
· Government showing commitment to fiscal consolidation, tax reforms
· Strong Political Mandate for Modi Government
The Sensex and the Nifty have been on a rally year to date and have touched record high levels in the month of September 2017. The Sensex and Nifty have declined by over 4% after reaching record high levels in the recent correction. The market was expecting a correction as liquidity other than fundamentals had driven the benchmark indices to return 18% year to date. The Sensex and Nifty continue to trade at a trailing price to earnings ratio of 24 and 26 respectively. The benchmark indices are trading at expensive valuations in the current scenario but expectations of earnings growth continue to keep the momentum more or less intact. Earnings growth for domestic companies have been mixed for the 1st quarter of 2017-18 but sectors where earnings growth have been strong such as transportation, retail, agri products, downstream oil & gas will continue to lead the markets forward.
Federal Reserve in its September policy meets kept interest rates unchanged but guided for 1 more rate hike in 2017 if inflation picks up. Fed also suggested that it could raise rates by two to three times in 2018 and 2019 if inflation holds to its own forecasts. Federal Reserve will also start unwinding its USD 4.5 trillion balance sheet in October 2017, initially by $10 billion per month, unwinding of the balance sheet could decrease the liquidity gradually. Fed’s clear forward guidance is positive for INR and 10-year G-sec and capital flows will continue into carry assets as markets factor in the cost of funds going forward.
Why growth is overriding other traditional parameters in equities
In this market investors are giving more importance for sustainable or disruptive growth and then reap the investment profits when the companies start showing significantly high profits. Considering that the market will continue to give a higher valuation to such stocks, companies with strong financial performance and strong track record will outshine their peers. A few examples of high growth companies are:
Avenue supermart
Since FY12 Avenue supermart exhibited strong top line growth of 40% and maintained an operating margin and net profit margin at levels of 4% and 3% respectively. Its current is P/E at 129 and market capitalization at Rs 696 billion.
Bajaj Finance
Bajaj finance is operating in Consumer Lending, SME Lending, Commercial Lending, Rural Lending, Fixed Deposits and Value Added Services. AUM has almost doubled in the last two years at Rs 689 billion, Continuous Net interest income growth is above 35% levels in the last 8 years.Its current P/BV is at 10.52 and Markt capitalization is t Rs 1060 billion.
Capacit’e Infraprojects
The company’s revenue has grown at a CAGR of 75% from FY14 to Rs. 11570 million in FY17. The Net Profit has grown at a CAGR of 157% in last four years to Rs. 696 million. Its current P/E is at 32 and market capitalization is at Rs 23 billion.
Thyrocare Technologies
Thyrocare is fully automated diagnostic laboratory with a focus on providing quality diagnostic testing at affordable costs to laboratories and hospitals in India and other countries with 26% revenue and 17.1% profit growth in the last 3 years. Its market capitalization is at Rs 36 billion and P/E is at 43.